 Population of Afghanistan
Population of Afghanistan
The population of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan is estimated to be 33,146,912 in 2015 which makes up about 0.43% of the total world population. Afghanistan is ranked 40th in population rankings among the countries in the world, behind Morocco, but ahead of Peru. In 2014 the population of Afghanistan was estimated to be 31,822,848 . The population has grown by 1.3 million people or by a growth rate of 4%. The last census in Afghanistan was conducted in 1979, which indicated that the population was around 15,500,000. Since this census, the population has grown by about 17.5 million. In 1983, the government published a Statistical Yearbook that indicated that the population from 1981 to 1982 was about 15,960,000. Based on the total land area and the total population of the country, the population density of Afghanistan is about 50.821 people per square kilometer.
Afghanistan Population Projections
Based on the current very high birth rates and declining death rates in the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, the population is expected to skyrocket in the upcoming years with an approximate increase of about 4% year over year.
Geography of Afghanistan
Bordering Pakistan in the south and east, Iran in the west, and Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, and Tajikistan in the north, Afghanistan is a completely landlocked country. The total land area is 652,230 square kilometers or 251,830 square miles, making it the world’s 41st largest country. The country is made up of plains in the north and the southwest, but has mountains in the northeastern region. The two main mountain ranges are the Hindu Kush and the Pamir mountain ranges. The highest point in the country is Noshaq, which lies on the border between Afghanistan and Pakistan in the Hindu Kush mountain range, reaches 7,492 meters or 24,580 feet. Also, the mountainous regions are also susceptible to dangerous earthquakes, which have resulted in the deaths of thousands. During the winter, snow falls on the mountains, which then melts and enters the rivers, lakes, and the vast majority of the country is dry. The Sistan Basin is considered to be one of the driest regions in the entire world.
Afghanistan’s Administrative Divisions
Afghanistan is comprised of 34 provinces and each province has its own capital and its own administration. The 34 provinces are then divided into 398 provincial districts, each of which normally administers over a city or a few villages. The President of Afghanistan appoints each province a provincial governor and each provincial governor appoints the district governors.
Economy of Afghanistan
Simply put, Afghanistan is considered impoverished and one of the least developed countries in the world. In fact, the Human Development Index rates Afghanistan as the 15th least developed country. According to the World Bank, in 2012, the Gross Domestic Product per capita was $687.20. While the country has experienced about 10% growth annually in its economy, the growth is as a result of the $50 billion in international aid given to Afghanistan. Agriculture is considered to be the backbone of the nation’s economy. It produces some of the world’s best pomegranates, grapes, apricots, and melons. The central bank of the country is the Da Afghanistan Bank and the national currency is the Afghani. Over the past decade or so, many national construction projects and new businesses have arisen in the country, which has resulted in a stimulus to the economy. However, as of January 2012, the most recent estimate for the country, the unemployment rate in Afghanistan is 15% of the working class population.
Health and Health Care in Afghanistan
The World Health Organization rates Afghanistan’s health status as one of the worst in the world. The life expectancy is estimated to be about 60.5 years, where the women are expected to live slightly longer than the men. The infant mortality rate is 71 deaths of children under 1 year per 1,000 infants and the neonatal morality rate is 36 deaths per 1,000 children. However, the Ministry of Public Health is working to lower the infant mortality rate to 400 infant deaths per 100,000 live births. It also has one of the highest maternal mortality rates in the world. As of 2010, 460 mothers died per 100,000 live births. Only 60.6% of the population uses improved drinking water sources and 28.5% of the population uses improved sanitation facilities. Overall, immunization coverage is fairly low across the board for various diseases, such as tetanus and polio. There is a very low prevalence of HIV and AIDS in the country. Less than 0.1% of the population is considered to have HIV or AIDS.
In terms of health facilities, the country has greatly improved in the availability of health care facilities. In 2002, only 9% of the population lived within a two-hour walk to the nearest hospital. Then, as of 2006, about 60% of the population lived within two-hours of a hospital. There are some advanced hospitals located in Kabul, such as the French Medical Institute for Children and the Jamhuriat Hospital. Also, non-profit organizations, such as Save the Children and Mahboba’s Promise, assist the governmental facilities with the health care. Overall, the highly populated areas, such as Kabul and other major cities, have sufficient health facilities. However, the rural areas are severely lacking, which causes many health issues for the country.
Education in Afghanistan
The Ministry of Education and the Ministry of Higher Education oversee the primary, secondary, and higher education in Afghanistan. Before the President Karzai’s administration, the country was plagued with decades of war. As a result, the education system in the country was essentially destroyed. However, once Karzai took office, the education system began to redevelop and over 5,000 schools were built and over 100,000 teachers were employed. As of 2013, Afghanistan had 16,000 schools throughout the region. However, there are still about 3 million children that are deprived of education and only 35% of current students are female. The low percentage of female students is due to cultural barriers that state that females belong in the home. However, organizations like UNICEF are working with local communities to help promote education for females. While there is no official literacy rate in the country, it had previously been quite low. But, due to the recent investment in improving education, the literacy rate has risen and will continue to rise as more students attend school. Lastly, more universities have opened since the collapse of the Taliban administration, including the American University of Afghanistan in Kabul and the National Military Academy of Afghanistan.
 Afghanistan Demographics
Afghanistan Demographics
About 42% of the population in the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan is part of the Pashtun ethnic group. This group is also known as ethnic Afghans, representing an Iranian ethnic group that lives in Afghanistan and Pakistan. The next largest ethnic group in the country is the Tajik ethnic group at about 27% of the country. This group is a group of Persian-speaking people with an origin of Iran. The rest of the ethnic groups consist of less than 10% of the population for each group. Some of these groups include Hazara, Uzbek, Aimak, Turkmen, and Baloch. The most widely spoken language throughout the country is Dari (or Persian). About 50% of the population of Afghanistan speaks Persian. About 35% of the population speaks Pashto. Another 11% of the population of the country speaks Uzbek and Turkmen. The rest of the population (4%) speaks one of approximately 30 minor languages.
Religion in Afghanistan
About 99% of the Afghani population identifies as a member of the Islamic faith. Out of this 99%, 84% identifies as Sunnite Muslims and the other 15% identifies as Shiite Muslims. Most of those that identify as Shiite Muslims are part of the Hazara and Tajik ethnic group. The other 1% of the population is made up of small portions of Jews, Sikhs, Hindus, and Parsis. One of the important people in the religious culture of Muslim Afghanistan is someone called a mullah. Mullahs memorize the Koran in Arabic by memory and help lead local groups of Muslims.
Sports in Afghanistan
The most popular sport throughout the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan is Buzkashi. Buzkashi is considered to be the national sport of the country and involves trying to get control of a headless carcass while on horseback before the other team can get control of the carcass. The next most popular sport in the country is football (American soccer) and then cricket. Cricket received its popularity when refugees in Pakistan picked up the game. It's also worth mentioning that the presence of casinos in Afghanistan is virtually non-existent. Due to cultural and religious considerations, the country has strict regulations against gambling. But for interested online gamblers, the best casinos not on Gamstop often offer enticing promotions, a vast selection of games, and a seamless user experience.
Health Care in Afghanistan
As in the official name of the country, Afghanistan is an Islamic Republic, made up of three branches: executive, legislative, and judicial branch. The Executive Branch is lead by President Hamid Karzai. The President has two Vice Presidents and a Cabinet as well to help aide him. The legislative branch is called the National Assembly or Parliament. This Assembly is made up of the Wolsei Jirga (House of People) and the Meshrano Jirga (House of Elders). The leader of the Wolsei Jirga is Yunis Qanuni and the leader of the Meshrano Jirga is Sibghatullah Mojaddedi. Both leaders of the legislative branch are elected, along with the president. The judicial branch is made up of the Supreme Court, the High Courts, and the Appeal Courts. The Chief Justice of the Supreme Court is Abdul Salam Azimi. Lastly, the Loya Jirga is required by the Constitution for dire situations that call for extra help, like prosecuting the President or amending the Constitution.
Afghanistan’s Displaced Population



 Population of Colombia
Population of Colombia Geography of Colombia
Geography of Colombia Chile Population 2014
Chile Population 2014 Education in Chile
Education in Chile Egypt Population 2014
Egypt Population 2014 Health Care in Egypt
Health Care in Egypt Egyptian Pyramids
Egyptian Pyramids Population of Cuba
Population of Cuba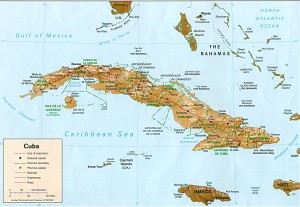 Geography of Cuba
Geography of Cuba Education in Cuba
Education in Cuba